Teamcenter, Siemens’ flagship Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software, is a powerhouse for managing product data throughout its entire lifecycle. From initial concept to final disposal, Teamcenter streamlines collaboration, improves efficiency, and ensures data integrity across teams and departments. It’s more than just a database; it’s a collaborative platform that connects everyone involved in a product’s journey, making it a crucial tool for engineering, manufacturing, and beyond.
Table of Contents
This exploration dives into Teamcenter’s functionality, integration capabilities, and best practices for implementation and administration.
We’ll cover everything from understanding the different Teamcenter versions and their features to mastering the core modules and customizing workflows to meet specific business needs. We’ll also address common troubleshooting issues and explore the future of Teamcenter within the ever-evolving PLM landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned PLM pro or just starting to explore Teamcenter, this guide offers valuable insights and practical advice.
Teamcenter Overview

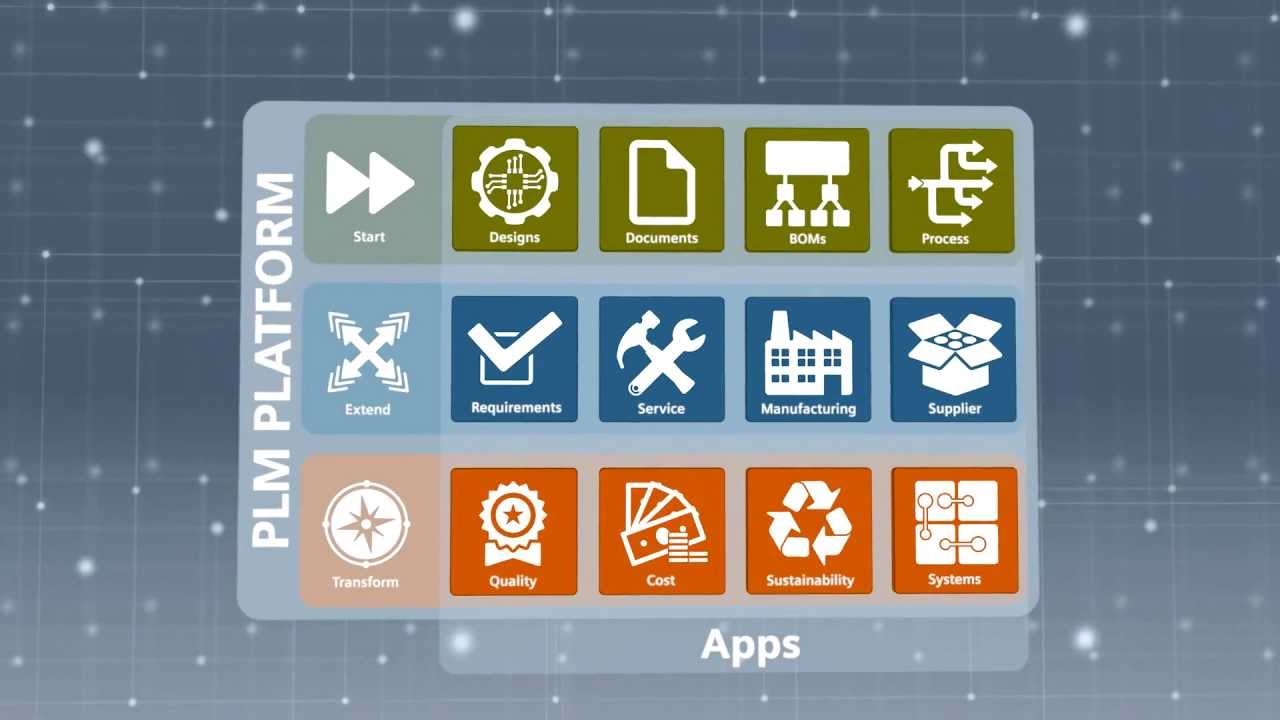
Teamcenter is Siemens’ flagship product lifecycle management (PLM) software. It’s basically a central hub for managing all the data related to a product’s lifecycle, from initial design concept to manufacturing and beyond. Think of it as a digital repository for everything involved in bringing a product to market, making collaboration and data management way easier.Teamcenter’s primary functions revolve around managing product data, processes, and collaboration.
This includes managing CAD models, documents, change orders, and other product-related information. It streamlines workflows, improves communication, and helps organizations make better decisions throughout the product development process.
Teamcenter Versions and Key Features
Different versions of Teamcenter cater to varying organizational needs and scales. While specific feature sets vary depending on the exact version and licensing, some common distinctions exist between the major offerings. For example, a smaller company might use a cloud-based, simplified version focusing on core data management, while a large multinational corporation might deploy a more extensive, on-premise version with advanced functionalities such as complex workflow automation and robust integration capabilities with other enterprise systems.
Key features often include advanced search and retrieval capabilities, version control, collaborative workflows, and robust reporting and analytics tools. These tools help organizations track progress, identify bottlenecks, and optimize their product development processes.
Teamcenter Users and Roles
A typical Teamcenter environment houses a variety of users, each with specific roles and responsibilities. These roles often reflect the organizational structure and the different stages of the product lifecycle. For example, engineers might use Teamcenter to manage and share CAD models and simulations, while project managers utilize it for tracking progress and managing tasks. Quality control personnel might leverage Teamcenter to access and manage inspection data, while manufacturing teams utilize it to access manufacturing documentation and work instructions.
Administrators are responsible for configuring and maintaining the system, ensuring data integrity and optimal performance. The system’s flexibility allows for customized roles and permissions, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data and perform specific actions.
Teamcenter Functionality
Teamcenter’s functionality revolves around its core modules, which work together to manage the entire product lifecycle. Understanding these modules and their interactions is key to leveraging the power of this PLM system. Think of it like a well-oiled machine – each part plays a crucial role, and their coordinated effort delivers a seamless workflow.Teamcenter’s core functionality is built upon a robust set of interconnected modules.
These modules aren’t isolated; they interact dynamically to provide a comprehensive PLM solution. The strength of Teamcenter lies in its ability to manage this complex interplay of data and processes.
Core Modules and Interdependencies
The primary modules within Teamcenter are tightly integrated to support various aspects of product development. For example, the Item Revision module, where product designs are managed, interacts closely with the Document Management module, where associated documentation like specifications and test results are stored. Changes made in one module automatically update related information in others, ensuring data consistency and traceability.
This integration minimizes errors and keeps everyone on the same page throughout the product lifecycle. Other key modules include Workflow Management, which governs the approval processes; Change Management, which tracks modifications and their impact; and BOM (Bill of Materials) Management, which details the components of a product. Each module is crucial and relies on the others to function effectively.
Workflow Processes Supported by Teamcenter
Teamcenter facilitates a wide array of workflow processes, all designed to streamline product development. These processes ensure that tasks are completed efficiently and according to established procedures. A common workflow might involve the design of a component, followed by its review and approval by multiple engineers, before finally being incorporated into the overall product design. Teamcenter automates much of this, routing documents for approval, tracking progress, and notifying relevant stakeholders of updates.
This automated approach significantly reduces delays and enhances team collaboration. Other examples include processes for managing change requests, releasing products, and handling non-conformance reports. The system’s flexibility allows for customization to fit specific company needs.
Examples of PLM Data Management in Teamcenter
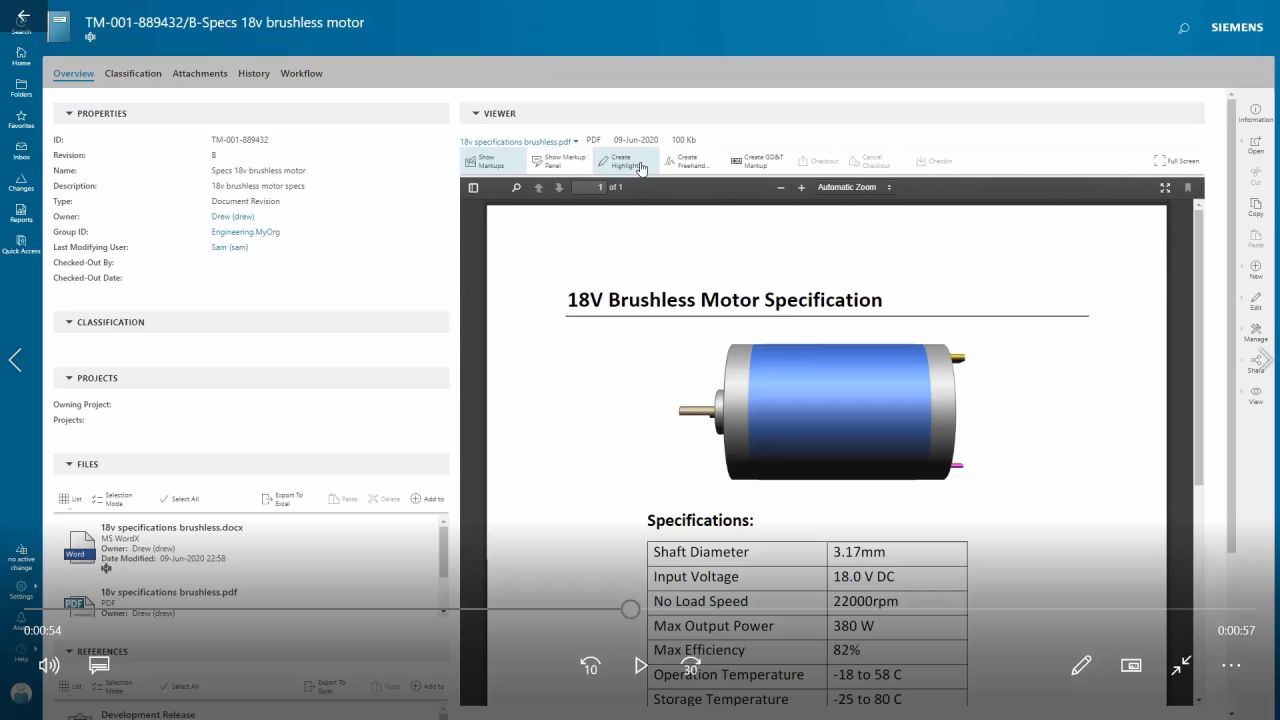
Teamcenter excels at managing various types of PLM data. Consider the design of a new automobile. Teamcenter would store the 3D CAD models of the car’s components, along with associated 2D drawings, specifications, and simulation results. The software also tracks revisions to these designs, allowing engineers to easily access previous versions and understand the evolution of the product.
Further, the system manages the bill of materials (BOM), detailing all the parts and their relationships. This ensures that all team members have access to the most current and accurate information, preventing costly errors during manufacturing. Teamcenter also manages the lifecycle of documents, ensuring proper version control and preventing the use of outdated information. Beyond CAD models, Teamcenter can also handle documents such as test reports, manufacturing instructions, and marketing materials, providing a centralized repository for all product-related information.
This centralized system ensures data integrity and traceability, crucial for compliance and efficient product development.
Teamcenter Integrations
Teamcenter’s power isn’t just in its own capabilities; it’s significantly amplified through its robust integration capabilities with other enterprise software. These integrations streamline workflows, improve data consistency, and ultimately boost overall engineering efficiency. Effectively leveraging these integrations is key to realizing the full potential of a Teamcenter implementation.Teamcenter’s integration capabilities offer numerous benefits, but also present some challenges.
Successful integration requires careful planning, resource allocation, and a deep understanding of both Teamcenter and the target systems. Mismatched data structures, conflicting workflows, and inadequate training can all lead to integration problems. However, the rewards – such as reduced manual data entry, improved data accuracy, and enhanced collaboration – often outweigh the challenges.
Common Teamcenter Integrations
Many common software systems integrate seamlessly with Teamcenter. These integrations cover a wide range of engineering and manufacturing applications. A successful integration strategy often considers the specific needs of an organization, prioritizing integrations that directly address key bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: Teamcenter integrates with leading CAD packages like Siemens NX, SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and Creo Parametric. This integration allows for direct management of CAD models and associated data within Teamcenter, eliminating the need for manual file transfers and version control headaches.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Systems: While Teamcenter itself is a PLM system, integration with other PLM systems might be necessary in complex, multi-system environments. These integrations often focus on data synchronization and collaborative workflows across different PLM platforms.
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): Integrating Teamcenter with MES allows for seamless transfer of product information and manufacturing instructions, improving traceability and streamlining production processes. This real-time data exchange minimizes delays and reduces errors.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Integrating Teamcenter with ERP systems like SAP or Oracle helps align engineering data with broader business processes, providing a more holistic view of product development and its impact on the overall organization. This integration facilitates better resource allocation and cost tracking.
- Document Management Systems: While Teamcenter has built-in document management capabilities, integration with other DMS might be beneficial for organizations with pre-existing systems or specific document handling requirements. This ensures consistent access to relevant documents across different platforms.
Benefits and Challenges of Teamcenter Integrations
The benefits of integrating Teamcenter with other platforms are substantial, ranging from improved efficiency to enhanced collaboration. However, potential challenges must be addressed proactively to ensure a smooth and successful integration.
- Benefits: Improved data consistency, reduced manual data entry, enhanced collaboration, streamlined workflows, better traceability, improved decision-making based on accurate and readily available data.
- Challenges: Data migration complexities, integration costs, potential for system conflicts, requirement for specialized expertise in both Teamcenter and the target system, the need for rigorous testing and validation, potential disruption during the integration process.
Hypothetical Integration Scenario: Teamcenter and a CAD Software
Let’s imagine a scenario where a company uses SolidWorks for CAD design and wants to integrate it with Teamcenter. Engineers design parts in SolidWorks, and upon completion, they check the models into Teamcenter. Teamcenter then manages revisions, approvals, and access control for these models. This integration allows for version control, collaborative design review, and automated workflows for part release.
For instance, when a design is approved in Teamcenter, it automatically triggers the generation of manufacturing documents, streamlining the handover to manufacturing. This seamless flow of information eliminates the risk of using outdated designs and improves overall product development efficiency. The challenge might lie in mapping SolidWorks’ data structures to Teamcenter’s, requiring careful configuration and potential data transformation.
However, the gains in efficiency and data integrity are substantial, justifying the investment in integration.
Teamcenter Implementation
Implementing Teamcenter, Siemens’ product lifecycle management (PLM) software, is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning and execution. A successful implementation hinges on a well-defined strategy, thorough data migration, and diligent project management. This section Artikels the key steps, considerations, and tasks involved in a smooth Teamcenter rollout.
Typical Steps in Teamcenter Implementation
Teamcenter implementation typically follows a phased approach. The initial phase focuses on defining project scope, identifying stakeholders, and establishing a clear project plan with defined timelines and resources. This is followed by a detailed requirements gathering phase, where the organization’s specific needs are analyzed and documented. Next comes the design and configuration phase, where the Teamcenter system is customized to meet those specific requirements.
This often involves configuring workflows, setting up security roles, and defining data structures. The subsequent phase involves testing and training. Rigorous testing ensures functionality and performance meet expectations, and comprehensive training equips users with the necessary skills. Finally, the system is deployed, and ongoing support and maintenance are provided to address any issues and ensure the system continues to meet the organization’s evolving needs.
This iterative process often involves feedback loops and adjustments throughout each phase to ensure a successful outcome.
Data Migration Considerations During Teamcenter Implementation
Data migration is a critical aspect of Teamcenter implementation. Organizations often possess large volumes of data from legacy systems, and transferring this data accurately and efficiently is paramount. Careful planning is crucial, including data cleansing, transformation, and validation. Data cleansing involves identifying and correcting inconsistencies or errors in the existing data. Transformation involves converting the data into a format compatible with Teamcenter.
Validation ensures data integrity after migration. The choice of migration strategy (e.g., big bang, phased approach) depends on factors like data volume, system complexity, and business criticality. For example, a phased approach might be preferred for organizations with massive datasets or complex legacy systems to minimize disruption. Thorough testing and validation are crucial throughout the migration process to identify and rectify any issues before the go-live date.
Post-migration support and monitoring are also necessary to ensure data integrity and system stability.
Essential Tasks for a Successful Teamcenter Rollout
A successful Teamcenter rollout requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive checklist. The following tasks are essential for a smooth implementation:
- Define clear project goals and objectives: Establish measurable goals that align with business needs.
- Identify and engage key stakeholders: Involve representatives from all affected departments to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan: Artikel timelines, resources, and responsibilities.
- Conduct thorough requirements gathering: Understand the organization’s specific needs and workflows.
- Design and configure the Teamcenter system: Customize the system to meet specific requirements.
- Perform rigorous testing and validation: Ensure system functionality and performance meet expectations.
- Provide comprehensive user training: Equip users with the skills to effectively utilize the system.
- Develop a comprehensive communication plan: Keep stakeholders informed throughout the implementation process.
- Establish a post-implementation support plan: Provide ongoing support and maintenance.
- Monitor system performance and address any issues promptly: Ensure system stability and user satisfaction.
Teamcenter Administration

Teamcenter administration is crucial for maintaining the health, performance, and security of your PLM system. A well-managed Teamcenter environment ensures smooth collaboration, data integrity, and efficient workflows for all users. Without proper administration, performance issues, security vulnerabilities, and user frustration can quickly arise, impacting the overall success of your PLM implementation.Teamcenter administrators are responsible for a wide range of tasks, from user management and system configuration to performance monitoring and troubleshooting.
They act as the gatekeepers of the system, ensuring its availability and usability for all stakeholders. Their expertise is vital in maximizing the return on investment of the Teamcenter software.
Responsibilities of a Teamcenter Administrator
Teamcenter administrators wear many hats. Their core responsibilities include managing user accounts, configuring system settings, monitoring system performance, implementing security measures, and providing technical support to users. They also handle database maintenance, backups, and upgrades, ensuring the long-term stability and reliability of the Teamcenter environment. Furthermore, they often play a key role in planning and executing system enhancements and integrations with other enterprise systems.
This often involves working closely with IT and other business units.
Common Administrative Tasks in Teamcenter
The day-to-day tasks of a Teamcenter administrator are diverse and demand a broad skill set. These tasks commonly include user account creation and modification, permission management, workflow configuration and monitoring, data management and cleanup, system performance tuning, and troubleshooting. Regular backups and disaster recovery planning are also critical components of their responsibilities. They also often manage system logs and reports to identify potential issues and trends.
Proactive monitoring prevents problems from escalating into major disruptions.
Configuring User Permissions in Teamcenter: A Step-by-Step Guide
Properly configuring user permissions is vital for data security and efficient workflow management. This process ensures that only authorized users can access specific data and perform certain actions within Teamcenter. Improperly configured permissions can lead to data breaches, workflow bottlenecks, and overall system instability. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify User Roles and Responsibilities: Before configuring permissions, clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each user or user group within the Teamcenter environment. This involves determining what data each user needs access to and what actions they are authorized to perform. For example, a design engineer might need full access to CAD models but only read access to financial data.
- Create or Modify User Accounts: In the Teamcenter administration interface, create user accounts or modify existing ones. This includes specifying user names, passwords, and other relevant information, such as email addresses and department affiliations. Many organizations use Active Directory integration for streamlined user management.
- Assign User Groups: Organize users into logical groups based on their roles and responsibilities. This simplifies permission management, allowing administrators to assign permissions to entire groups rather than individual users. For example, you might create groups like “Design Engineers,” “Manufacturing Engineers,” and “Project Managers.”
- Define Access Rights: Assign appropriate access rights to each user group. This involves specifying which objects and actions users within each group are permitted to perform. Teamcenter provides a granular level of control, allowing administrators to define permissions at the object level, such as specific folders or item types. This level of control is crucial for maintaining data integrity and security.
- Test and Validate Permissions: After configuring permissions, thoroughly test and validate them to ensure they function as intended. This may involve logging in as different users and verifying their access rights. Testing is crucial to identify and correct any errors or inconsistencies before they impact the overall system.
- Document Permission Structure: Maintain thorough documentation of the permission structure. This documentation should clearly Artikel the access rights of each user group and the rationale behind those permissions. This ensures consistency and simplifies troubleshooting in the future.
Teamcenter Customization
Teamcenter’s strength lies not just in its out-of-the-box functionality, but also in its impressive customization capabilities. This allows companies to tailor the system to precisely match their unique workflows, data structures, and reporting needs, maximizing efficiency and integration with existing processes. Effectively leveraging Teamcenter’s customization features is key to unlocking its full potential and achieving a truly optimized PLM solution.Teamcenter offers a robust set of tools and techniques for customization, ranging from simple configuration changes to complex code modifications.
These customizations can dramatically improve user experience, streamline processes, and enhance data management. This flexibility ensures that Teamcenter adapts to the business, rather than the other way around.
Workflow Customization Techniques
Customizing Teamcenter workflows involves modifying the pre-defined processes to better suit specific business requirements. This often entails adjusting the sequence of tasks, adding or removing steps, changing approvals, and integrating with external systems. For example, a company might customize the change order workflow to include a mandatory review step by a regulatory compliance officer before approval, or integrate it with their ERP system for automated cost tracking.
This is typically achieved through Teamcenter’s workflow editor, a graphical tool that allows users to visually design and modify workflows without requiring extensive coding knowledge. More complex modifications might involve scripting using languages like Java or other supported languages. The key is to strike a balance between customization and maintainability; overly complex customizations can become difficult to manage and update over time.
Custom Report Design for Project Metrics
Creating custom reports is crucial for tracking key project metrics and providing management with valuable insights. Teamcenter allows users to define custom reports to display specific data related to project progress, resource allocation, and quality control. For instance, a project manager might create a custom report showing the status of all tasks within a specific project, highlighting any delays or issues.
Another example would be a report visualizing the number of design changes made over time, potentially correlated with the cost of those changes. This data visualization can help identify trends and improve future project planning. This functionality is often achieved through Teamcenter’s reporting tools, which provide pre-built templates and the ability to create customized queries and visualizations. The ability to export these reports in various formats (like Excel or PDF) is crucial for wider distribution and analysis within the organization.
Examples of Teamcenter Customization for Specific Business Needs
Several examples showcase how Teamcenter customization addresses unique business challenges. A manufacturing company might customize Teamcenter to integrate with their shop floor equipment, enabling real-time tracking of production progress and automatic updates to the PLM system. An aerospace company might customize the system to manage complex assembly instructions and maintain detailed traceability of parts throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring regulatory compliance.
A pharmaceutical company might customize the system to manage regulatory documentation and track the entire lifecycle of a drug, from research and development to manufacturing and distribution. These customizations are tailored to meet the specific industry requirements and regulatory compliance needs of each company, demonstrating the adaptability of Teamcenter to diverse business contexts.
Teamcenter Security
Teamcenter’s security is paramount, ensuring only authorized users can access and modify sensitive product development data. A robust security model protects intellectual property and maintains data integrity throughout the product lifecycle. This section details the key security features and best practices for a secure Teamcenter environment.Teamcenter employs a multi-layered security approach, combining authentication, authorization, and data encryption to safeguard information.
Access control is granular, allowing administrators to define permissions at various levels, from individual users to entire groups. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific data, functionalities, and processes.
Authentication Methods
Teamcenter supports various authentication methods, including Windows authentication, LDAP integration, and its own internal user management system. This flexibility allows seamless integration with existing enterprise infrastructure and provides a robust authentication process. Choosing the appropriate method depends on the existing IT infrastructure and security policies. For example, leveraging Windows authentication simplifies user management by using existing domain credentials.
LDAP integration offers centralized user management for larger organizations.
Authorization and Access Control
Teamcenter’s authorization mechanism is based on roles and permissions. Administrators assign specific roles to users, granting them access to certain functionalities and data based on their responsibilities. This granular control ensures that only authorized personnel can perform specific actions, preventing unauthorized access and modification of sensitive information. Permissions can be further refined using item-level security, which allows administrators to control access to specific items within Teamcenter.
Data Encryption
Teamcenter offers data encryption at rest and in transit to protect sensitive data. Data encryption at rest protects data stored on the Teamcenter database, while encryption in transit protects data during transmission between clients and the server. This dual-layered encryption ensures that data remains secure even if the database or network is compromised. Implementing strong encryption algorithms is crucial for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity.
Teamcenter’s a pretty robust PLM system, but sometimes you need to distill complex data for presentations. That’s where creating killer slides with microsoft power point comes in handy; you can easily visualize Teamcenter’s insights, making them super clear for stakeholders. Then, bam, you’ve got a presentation that’ll impress anyone. Back to Teamcenter – it’s all about efficient data management, after all.
Best Practices for Securing Teamcenter
Implementing robust security practices is vital for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of Teamcenter data. Regular security audits, strong password policies, and user training are crucial for minimizing security risks. These practices help ensure that the system remains secure and that data is protected from unauthorized access. It’s also essential to stay updated with the latest security patches and updates to address potential vulnerabilities.
Teamcenter User Roles and Permissions
The following table Artikels some common Teamcenter user roles and their associated permissions. Note that these are examples and the specific permissions can be customized based on organizational needs.
| Role | Data Access | Functionality | Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Administrator | Full Access | Full Access | Full Access |
| Project Engineer | Access to project-related data | Create, modify, and approve documents and parts | Limited access |
| Data Manager | Access to specific data sets | Manage data lifecycles and workflows | Limited access to data management features |
| Viewer | Read-only access to specific data | Limited functionality, primarily viewing data | No access |
Teamcenter Troubleshooting
Teamcenter, while a powerful PLM system, isn’t immune to hiccups. Understanding common issues and effective troubleshooting techniques is crucial for maintaining productivity and preventing project delays. This section will cover some frequently encountered problems and their solutions, focusing on practical approaches you can use to get back on track quickly.
Common Teamcenter Errors and Solutions
Many Teamcenter errors stem from seemingly minor issues. Addressing these proactively can save significant time and frustration. The following list details some common errors and their solutions.
- Error: “Connection to Teamcenter Server Failed.” This is often due to incorrect server address, port number, or network connectivity problems.
- Solution: Verify your Teamcenter client configuration settings, ensuring the server address and port are correct. Check your network connection and firewall settings to ensure that communication with the Teamcenter server is not blocked. Consider restarting your computer and the Teamcenter client.
- Error: “Insufficient Privileges.” This occurs when a user attempts an action they don’t have permission to perform.
- Solution: Check the user’s roles and permissions within Teamcenter. A Teamcenter administrator can modify the user’s access rights to grant the necessary permissions.
- Error: “File Check-in/Check-out Conflicts.” This arises when multiple users attempt to modify the same file simultaneously.
- Solution: Teamcenter’s version control system handles these conflicts, but it’s crucial to understand the resolution process. The system might offer options like merging changes or creating a new version. Clear communication within the team about file access and modifications is essential to minimize conflicts.
- Error: “Database Errors.” These can range from simple connection issues to more complex database integrity problems.
- Solution: These require more in-depth investigation. Check Teamcenter’s logs for specific error messages, and involve your IT or Teamcenter administrator. They might need to run database diagnostics or perform database maintenance tasks.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems
Connectivity issues are a common source of frustration. These problems can manifest in various ways, ranging from slow performance to complete disconnection.
- Problem: Slow performance. This could be due to network congestion, server overload, or issues with the Teamcenter client itself.
- Solution: Check your network bandwidth and server load. If the problem persists, try restarting the Teamcenter client or your computer. Consider contacting your IT department to rule out network-related problems. Optimizing Teamcenter client settings, such as caching strategies, might also improve performance.
- Problem: Intermittent disconnections. This often indicates network instability or firewall issues.
- Solution: Check your network connection for stability. Verify firewall settings to ensure that Teamcenter is allowed to communicate. If using a VPN, ensure it is properly configured and connected.
- Problem: Complete inability to connect. This points to either a server outage, network problems, or client configuration errors.
- Solution: First, check the status of the Teamcenter server. If the server is down, wait for it to be restored. If the server is operational, check your network connection and Teamcenter client configuration. If you are still unable to connect, contact your IT or Teamcenter administrator.
Teamcenter Future Trends
Teamcenter, like all PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) software, is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. The digital transformation sweeping industries is pushing PLM solutions toward greater integration, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Teamcenter’s future will be defined by its ability to adapt to these trends and leverage emerging technologies to enhance its core functionalities. This involves not just incremental improvements but also a fundamental shift towards a more connected, intelligent, and user-friendly platform.The landscape of PLM is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established players and agile startups vying for market share.
Teamcenter’s continued success hinges on its ability to innovate and stay ahead of the curve. This includes integrating cutting-edge technologies like AI, machine learning, and blockchain, while simultaneously improving user experience and streamlining workflows. Siemens, the developer of Teamcenter, is actively investing in these areas, positioning Teamcenter to remain a dominant force in the PLM market.
Enhanced AI and Machine Learning Integration
Teamcenter’s future will see a significant increase in the use of AI and machine learning to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance overall efficiency. For example, AI-powered predictive maintenance could analyze sensor data from manufacturing equipment to anticipate potential failures and schedule preventative maintenance, minimizing downtime. Machine learning algorithms could analyze historical data to optimize design processes, identify potential design flaws early on, and even suggest improved designs.
This level of automation will reduce human error, accelerate product development cycles, and improve product quality. Imagine, for instance, a system that automatically flags potential design conflicts based on past project data, saving engineers valuable time and resources.
Improved User Experience and Interface
A key area of focus for future Teamcenter versions will be enhancing the user experience. This includes a more intuitive interface, simplified workflows, and improved accessibility across various devices. Siemens has already made strides in this direction with recent releases, but further improvements are expected, potentially incorporating features like natural language processing for easier data searching and retrieval.
The goal is to make Teamcenter more user-friendly for engineers, designers, and other stakeholders, regardless of their technical expertise. Think of a simplified dashboard that provides at-a-glance insights into project progress, potential risks, and key performance indicators.
Advanced Data Management and Analytics
Future Teamcenter versions will likely incorporate more sophisticated data management and analytics capabilities. This involves improved data visualization tools, advanced reporting features, and enhanced integration with other enterprise systems. The ability to extract meaningful insights from vast amounts of product data will be crucial for data-driven decision-making. For example, a comprehensive dashboard could track key metrics such as product cost, development time, and quality control data, allowing management to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions.
This data-driven approach will enable companies to optimize their product development processes and gain a competitive advantage.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication Tools
Teamcenter will continue to evolve its collaboration features to facilitate seamless communication and information sharing among team members, regardless of their location. This includes improved integration with communication platforms, enhanced version control capabilities, and more robust document management features. Consider a system that automatically notifies relevant stakeholders of design changes or critical updates, eliminating communication bottlenecks and improving project coordination.
This enhanced communication will significantly improve teamwork and accelerate product development.
Expanded Integration with IoT and Digital Twin Technologies
The integration of Teamcenter with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and digital twin technologies is another key trend. This will enable real-time monitoring of product performance, predictive maintenance, and improved product design based on real-world usage data. Imagine a scenario where sensor data from a deployed product is automatically fed into Teamcenter, providing valuable insights into its performance and allowing engineers to identify potential design improvements for future iterations.
This integration will create a closed-loop system that continuously improves product design and performance.
Final Wrap-Up
Teamcenter offers a comprehensive solution for managing the complexity of modern product development. By understanding its core functionalities, integrating it effectively with existing systems, and implementing robust security measures, organizations can leverage Teamcenter to optimize their processes, improve collaboration, and ultimately, bring better products to market faster. The key takeaway is that Teamcenter is not just software; it’s a strategic investment in streamlined product development and improved organizational efficiency.
Mastering its capabilities is key to unlocking its full potential and gaining a competitive edge.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between Teamcenter and other PLM systems?
Teamcenter distinguishes itself through its extensive functionality, scalability, and robust integration capabilities. While other systems might focus on specific aspects of PLM, Teamcenter offers a comprehensive, end-to-end solution.
How much does Teamcenter cost?
Teamcenter pricing is highly variable and depends on factors like the number of users, modules implemented, and required support services. Contact Siemens directly for a customized quote.
Is Teamcenter cloud-based or on-premise?
Teamcenter offers both cloud-based (Teamcenter X) and on-premise deployment options, allowing organizations to choose the solution best suited to their infrastructure and security needs.
What kind of training is available for Teamcenter?
Siemens offers a range of training options, from instructor-led courses to online tutorials and self-paced learning materials, covering various aspects of Teamcenter functionality and administration.
What are the system requirements for Teamcenter?
System requirements vary depending on the Teamcenter version and deployment method (cloud vs. on-premise). Check Siemens’ official documentation for the most up-to-date specifications.

